
Moderators: Elvis, DrVolin, Jeff
The importance of Early Ambulatory Multidrug Treatment
Talk Title: Multifaceted Highly Targeted Sequential Multidrug Treatment of Early Ambulatory High-Risk SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19)
Internist, cardiologist, and Professor of #Medicine at Texas A & M College of Medicine, Dallas, TX USA. Since the outset of the pandemic, Dr. McCullough has been a leader in the medical response to the COVID-19 disaster and has published “#Pathophysiological Basis and Rationale for Early Outpatient Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection” the first synthesis of sequenced multidrug treatment of ambulatory patients infected with #SARS-CoV-2 in the American Journal of Medicine and subsequently updated in Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine. He has 35 peer-reviewed publications on the infection and has commented extensively on the medical response to the COVID-19 crisis in TheHill

alloneword » Fri Dec 24, 2021 12:04 am wrote:I wonder why they didn't include it?
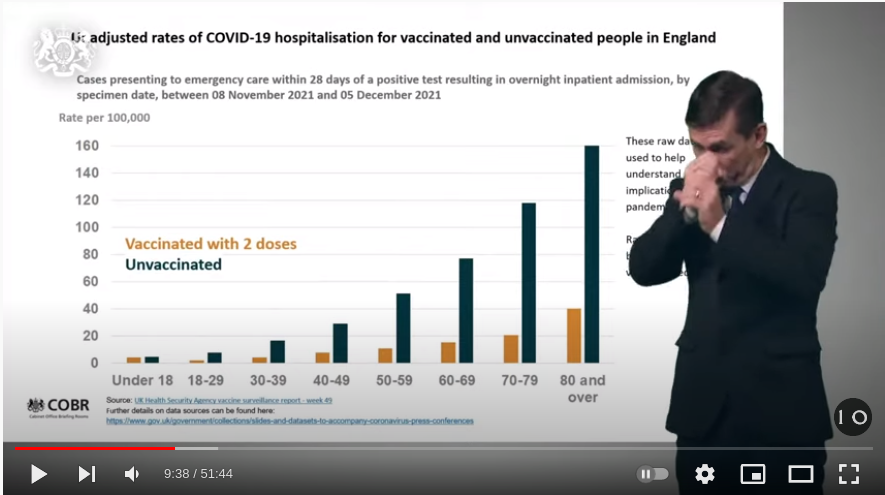
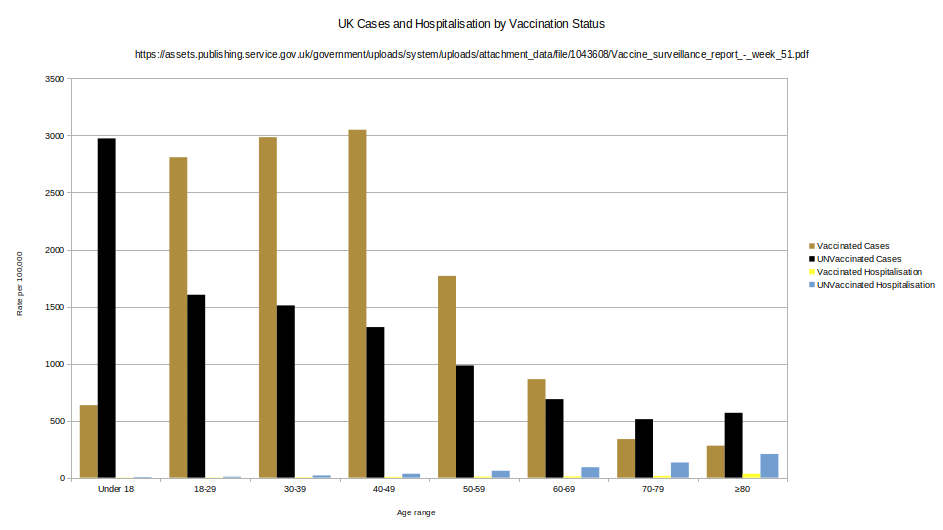
Cases presenting to emergency care (within 28 days of a positive test) resulting in overnight inpatient admission, by specimen date between week 47 and week 50 2021
(pg. 11)Uninfected individuals cannot transmit; therefore, the vaccines are also effective at preventing transmission.
Open the book to a random page and start reading. Then realize there are ~450 other pages with stories of corruption just as bad as the one you just randomly selected.

Change to use of modelling for headline estimates, based on midpoint of week. Headline figures not comparable to previous estimates.
COVID-19 Coronavirus spike protein analysis for synthetic vaccines, a peptidomimetic antagonist, and therapeutic drugs, and analysis of a proposed achilles’ heel conserved region to minimize probability of escape mutations and drug resistanceAbstract
This paper continues a recent study of the spike protein sequence of the COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2). It is also in part an introductory review to relevant computational techniques for tackling viral threats, using COVID-19 as an example. Q-UEL tools for facilitating access to knowledge and bioinformatics tools were again used for efficiency, but the focus in this paper is even more on the virus. Subsequence KRSFIEDLLFNKV of the S2′ spike glycoprotein proteolytic cleavage site continues to appear important. Here it is shown to be recognizable in the common cold coronaviruses, avian coronaviruses and possibly as traces in the nidoviruses of reptiles and fish. Its function or functions thus seem important to the coronaviruses. It might represent SARS-CoV-2 Achilles’ heel, less likely to acquire resistance by mutation, as has happened in some early SARS vaccine studies discussed in the previous paper. Preliminary conformational analysis of the receptor (ACE2) binding site of the spike protein is carried out suggesting that while it is somewhat conserved, it appears to be more variable than KRSFIEDLLFNKV. However compounds like emodin that inhibit SARS entry, apparently by binding ACE2, might also have functions at several different human protein binding sites. The enzyme 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 is again argued to be a convenient model pharmacophore perhaps representing an ensemble of targets, and it is noted that it occurs both in lung and alimentary tract. Perhaps it benefits the virus to block an inflammatory response by inhibiting the dehydrogenase, but a fairly complex web involves several possible targets.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7151553/
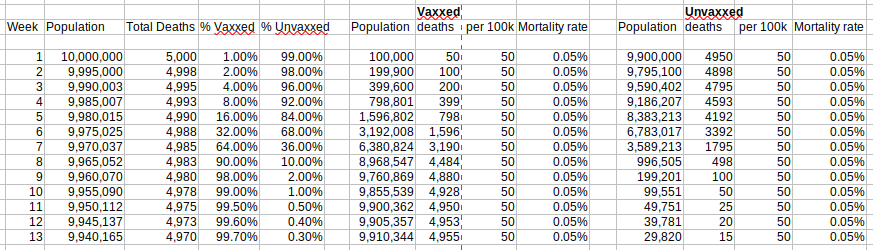
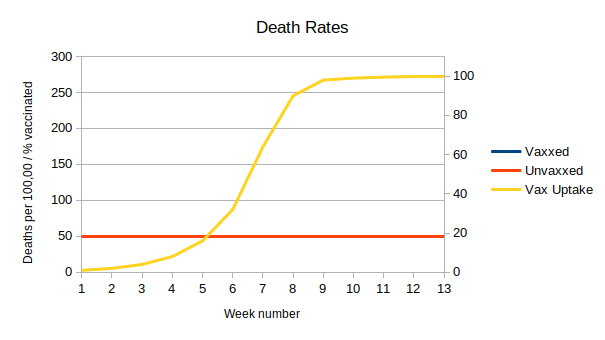
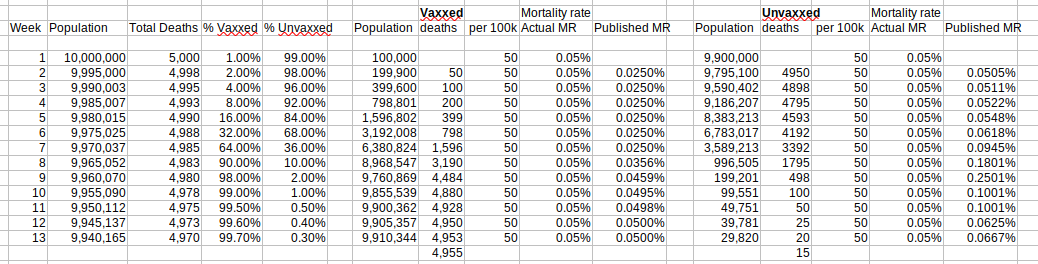

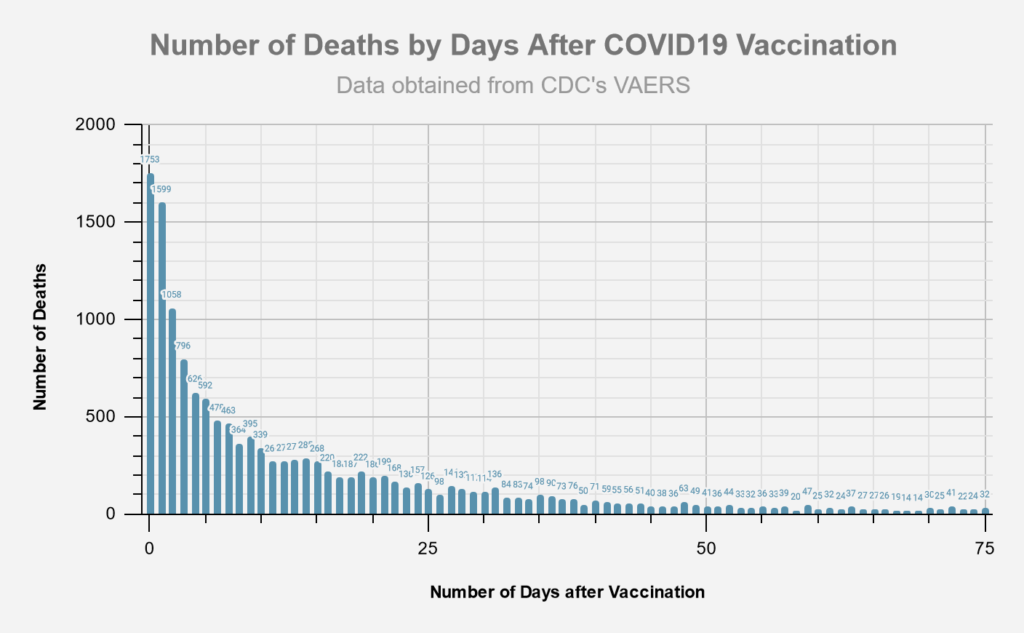
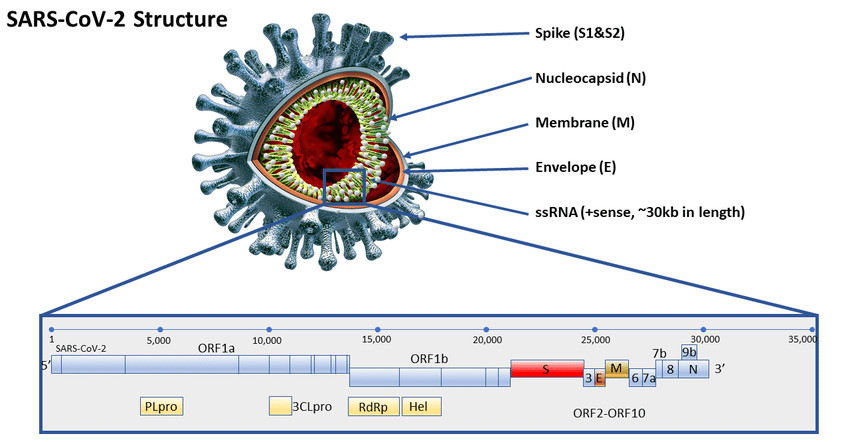
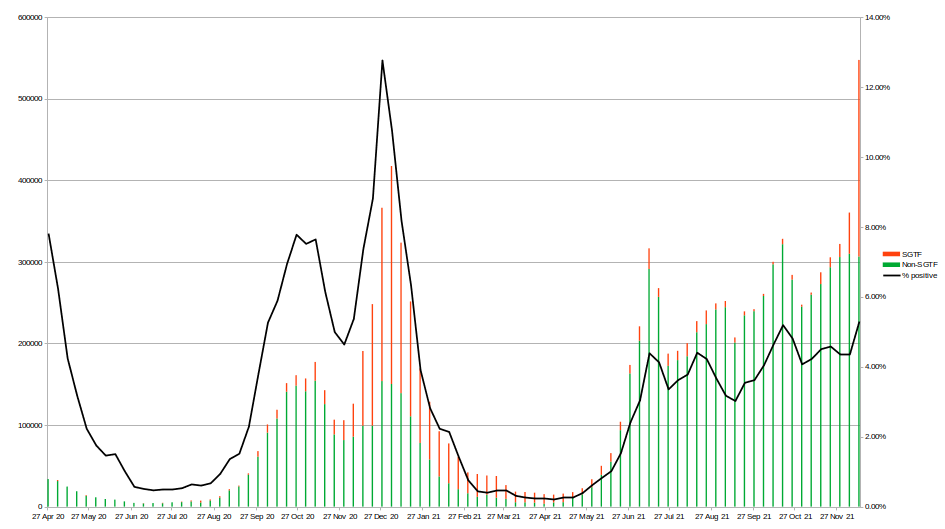

Return to Data & Research Compilations
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 1 guest